ASTRONOMY

ASTRONOMY
Space Science
- Astronomy= The branch of science which deals with celestial objects, space, and the physical universe as a whole
- Astrology= The study of the movements and relative positions of celestial bodies interpreted as having an influence on human affairs and the natural world. (horoscopes)
- Cosmos = The universe
- Cosmology= The study of the movements and relative positions of celestial bodies interpreted as having an influence on human affairs and the natural world.
- Astronomer= An expert in or student of astronomy.
- Astronaut= A person who is trained to travel in a spacecraft.
- Cosmonaut= A Russian astronaut.
- Astrophysics= the branch of astronomy concerned with the physical nature of stars and other celestial bodies, and the application of the laws and theories of physics to the interpretation of astronomical observations.
Celestial bodies
Celestial bodies or heavenly bodies are objects in space such as the sun, moon, planets, and stars. They form a part of the vast universe we live in and are usually very far from us.
- Galaxy = A huge collection of gas, dust and billions of stars and their solar systems held together by gravity.
- Milky Way =Our galaxy that contains over 200 billion stars.
- Solar System= The collection of eight planets and their moons in orbit round the sun, together with smaller bodies in the form of asteroids, meteoroids, and comets.
- Planet= a celestial body moving in an elliptical orbit round a star.
- Solar System Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
- Inner Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are the planets closest to the Sun. They are called the inner planets which are made up mostly of rock.
- Outer Planets: The outer planets are gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and ice giants Uranus and Neptune.
- Dwarf Planet= a celestial body resembling a small planet but lacking certain technical criteria that are required for it to be classed as such.
- Dwarf Planets: Pluto, Eris, Ceres, Makemake, Haumea

- Asteroid= A small rocky body orbiting the sun. Large numbers of these, ranging enormously in size, are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, though some have more eccentric orbits.
- Asteroid Belt= The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, called asteroids or minor planets.

- Meteor= A small body of matter from outer space that enters the earth’s atmosphere.
- Meteorite= A piece of rock or metal that has fallen to the earth’s surface from outer space as a meteor.


- Crater= A cavity in the ground of a celestial object, typically caused by explosions or meteor impact.

- Comet= A celestial object consisting of a nucleus of ice and dust and, when near the sun, a ‘tail’ of gas and dust particles pointing away from the sun.
- Star= An astronomical object made of bright, glowing matter called plasma. They’re held together by gravity and are incredibly hot
- Shooting star= Streaks of light in the sky that occur when meteoroids fall into the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up.

- binary star= A system of two stars where one revolves around the other or both revolve around a common center.
- Dwarf star = A small star with low luminosity.
- Starburst = A period of intense activity in a galaxy where lots of stars are formed.
- Moon = A large celestial object that acts as a natural satellite to Earth. Most planets in our solar system have at least one moon and some have several.
- Solar= Relating to or determined by the sun.
- Lunar=Of, determined by, or resembling the moon.
- Interstellar= Occurring or situated between stars
- The difference between stars and planets: Planets in orbits spin on their own axis and change their positions constantly. Stars consist of matter like Hydrogen, Helium, and other light elements. Planets, on the other hand, contain solids, liquids, gases, or a combination thereof.
- The difference between meteor and meteorite: Think of them as “space rocks.” When meteoroids enter Earth’s atmosphere (or that of another planet, like Mars) at high speed and burn up, the fireballs or “shooting stars” are called meteors. When a meteoroid survives a trip through the atmosphere and hits the ground, it’s called a meteorite.
- Supernova= A star that suddenly increases greatly in brightness because of a catastrophic explosion that ejects most of its mass
- Big Bang = The main theory explaining how the universe started. It states that 13.8 billion years ago, space expanded quickly to form the atoms that would produce stars and galaxies.
- Nebula= a cloud of gas and dust in outer space, visible in the night sky either as an indistinct bright patch or as a dark silhouette against other luminous matter.


- Black hole: A place in space where the pull of gravity is so strong that even light can’t get out.
- Eclipse: An obscuring of the light from one celestial body by the passage of another between it and the observer or between it and its source of illumination.


- Moon phases: Astronomers have broken down this cycle into four primary Moon phases: New Moon, First Quarter, Full Moon, and Last Quarter. There are also four secondary phases: Waxing Crescent, Waxing Gibbous, Waning Gibbous, and Waning Crescent.
- Waning= When the moon becomes gradually less visible.
- Waxing= When the moon becomes gradually more visible.

- Constellation= A group of stars forming a recognizable pattern that is traditionally named after its apparent form or identified with a mythological figure.
- Big Dipper= Constellation of the seven brightest stars of the larger constellation Ursa Major.

Dark matter = Particles thought to exist in space that don’t absorb, reflect or emit light, and thus can’t be observed.
Rockets
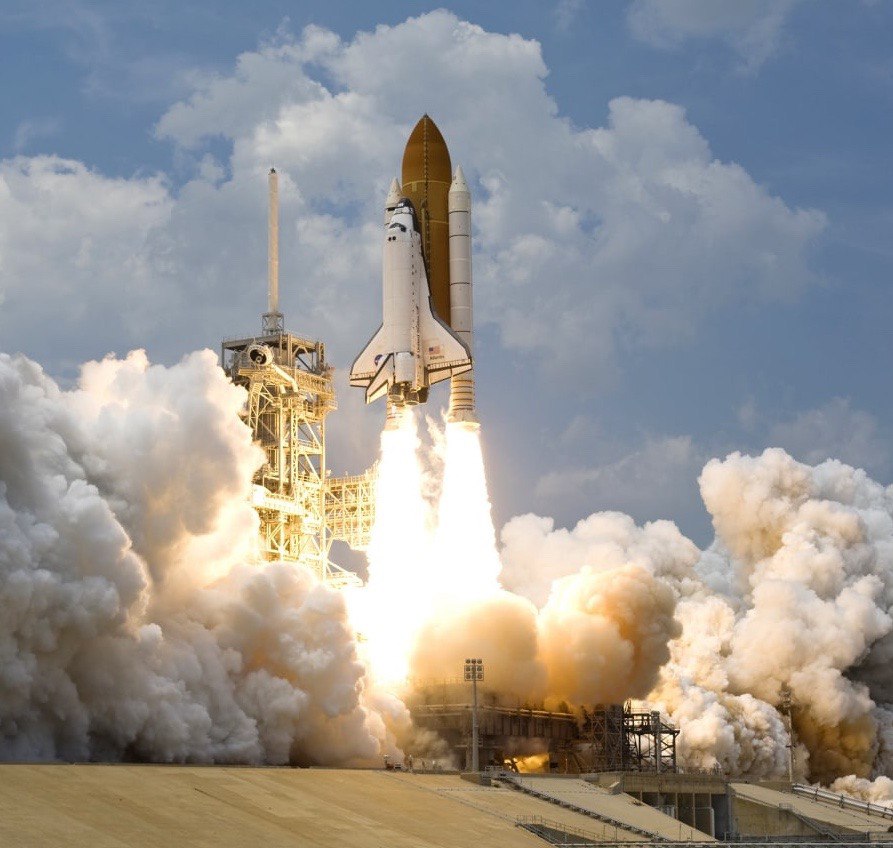
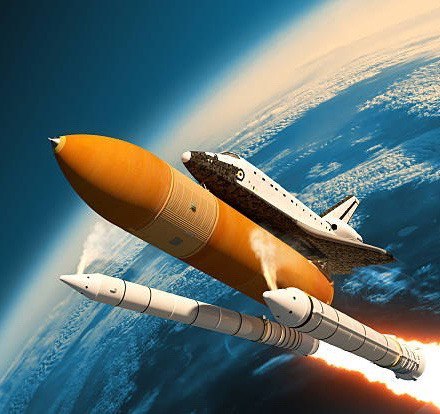
- space shuttle= A rocket-launched spacecraft able to land like an unpowered aircraft, used to make repeated journeys between the earth and space.
- rocket= A vehicle designed to carry people into space.
- launch = blast off= thrust = To send a rocket, missile, or satellite into the air or space.
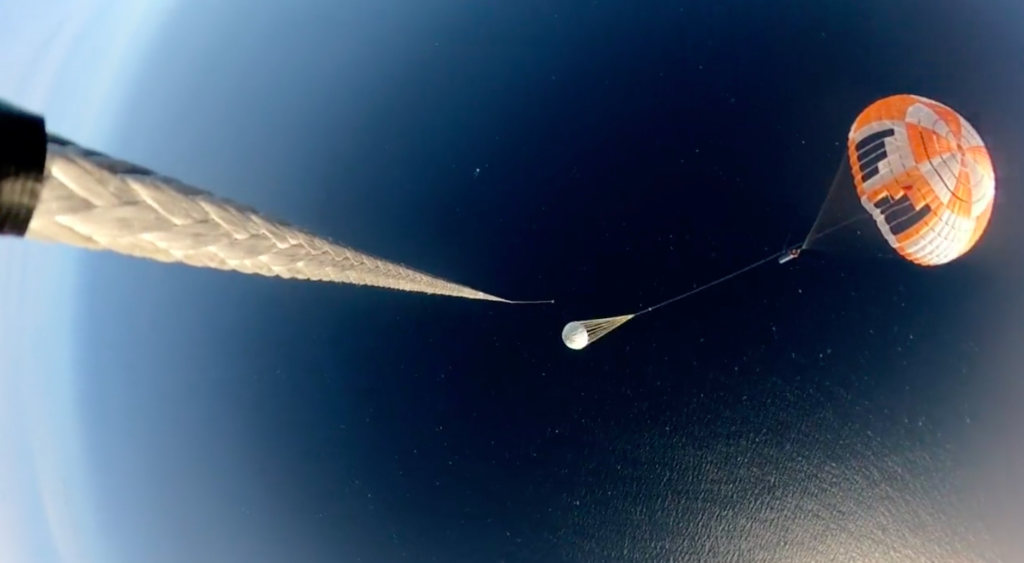
- booster rocket= A booster rocket (or engine) is either the first stage of a multistage launch vehicle, or else a shorter-burning rocket used in parallel with longer-burning .
- booster parachute= A parachute which helps the booster rocket lands.
- satellite= An artificial body placed in orbit round the earth or moon or another planet in order to collect information or for communication.



Orbital Litter
- space debris= Defunct human-made objects in space—principally in Earth orbit—which no longer serve a useful function. It is also called orbital litter or space junk. They are the leftover of satellites and spacecrafts that orbit in space. They are classified as small-sized, big-sized, and medium-sized debris and among them the medium sized ones are so dangerous because of their tremendous speed.

Aliens
- UFO= A mysterious object seen in the sky for which it is claimed no orthodox scientific explanation can be found, often supposed to be a vehicle carrying extraterrestrials. It stands for Unidentified Flying Object.
- Flying Saucer= A disc-shaped flying craft supposedly piloted by aliens; a UFO.
- Extraterrestrial creature= A hypothetical or fictional being from another world. They are also called aliens.


Other relevant vocabulary items to space
- sphere = A round solid figure, or its surface, with every point on its surface equidistant from its center.
- hemisphere= A half of the earth or any sphere, usually as divided into northern and southern halves by the equator, or into western and eastern halves by an imaginary line passing through the poles.
- atmosphere =The envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet.
- apogee= zenith= The point in the sky or celestial sphere directly above an observer. / the highest point reached by a given celestial object.
- nadir= The point on the celestial sphere directly below an observer. / the lowest point
- gravity= The force that attracts a body towards the center of the earth, or towards any other physical body having mass.
- weightlessness= The state of apparently not being acted on by gravity; the state of being weightless.
- luminosity= The intrinsic brightness of a celestial object (as distinct from its apparent brightness diminished by distance).
- halo= A circle of white or colored light around the sun, moon, or other luminous body caused by refraction through ice crystals in the atmosphere.
- radiation= The emission of energy as electromagnetic waves or as moving subatomic particles, especially high-energy particles which cause ionization
- spectrum= A band of colors, as seen in a rainbow, produced by separation of the components of light by their different degrees of refraction according to wavelength.
- vacuum= A space entirely devoid of matter.
- Light year= The distance light travels in one year (nearly 6 trillion miles).
- observatory = A building equipped with materials to make astronomical observations.
- telescope= An instrument that allows us to see into space.
- magnitude= The great size or extent of something
- mass – How much material an object is made up of, as opposed to weight which measures the pull of gravity on an object.
- infinity= The concept of something that is unlimited, endless, without bound.
- turbulence = Violent or unsteady movement of air or water, or of some other fluid.
- orbit= A regular and repeating circuit that one celestial object takes around another.
- revolve= Move in a circle on a central axis.
- rotate= Move or cause to move in a circle round an axis or center.
- spin= turn or cause to turn or whirl round quickly.
- elliptical orbit = One object revolving around another in an oval shape. The shape is known as an ellipse.
- astronomical unit = A unit of measurement that’s roughly the distance from the Earth to the Sun (93 million miles).

